The Basics of Structural Steel Construction
Understanding Structural Steel
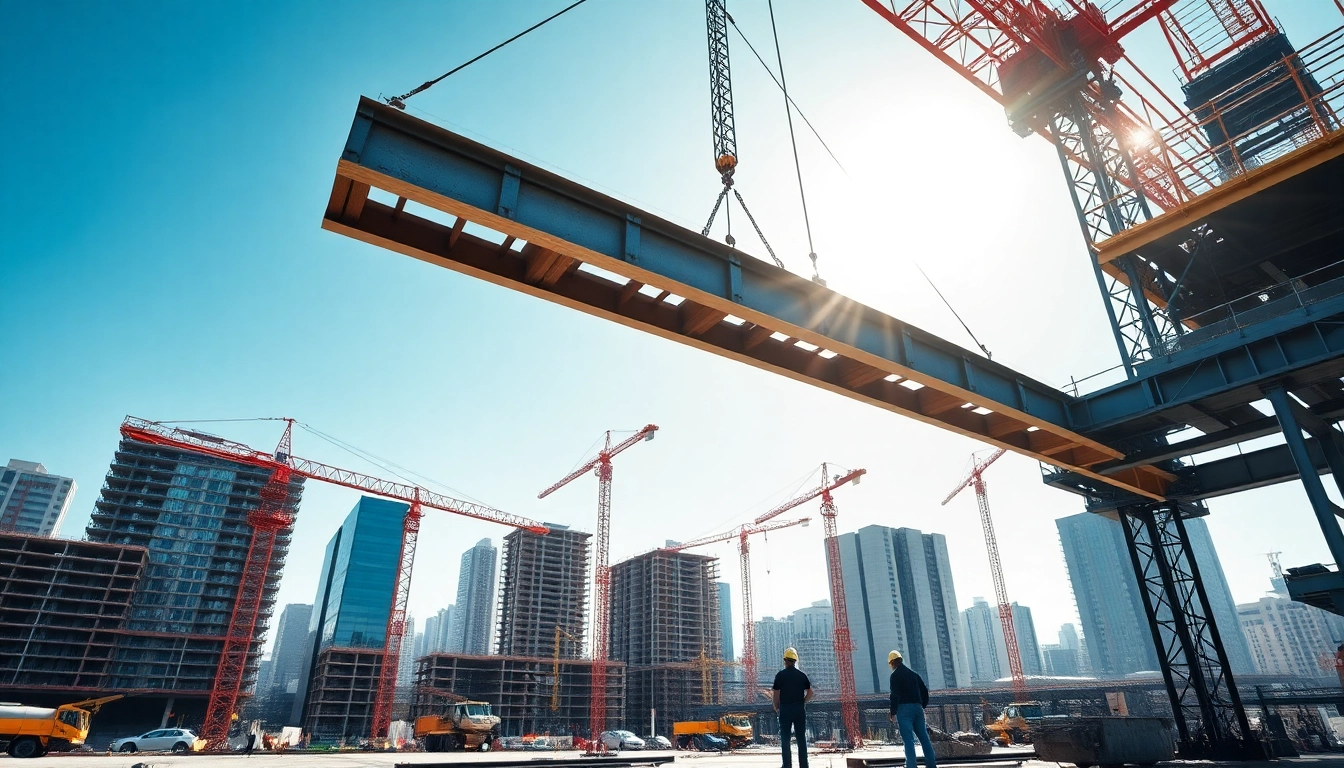
Structural steel is a fundamental material in construction, known for its impressive strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. Made primarily from iron and carbon, it is designed to withstand significant loads, making it ideal for various applications such as building frameworks, bridges, and industrial facilities. One of the distinctive features of structural steel is its ability to be precisely fabricated and shaped into a variety of forms, allowing engineers and architects to create complex structures that meet modern aesthetic and functional requirements. The production process often follows stringent industry standards to ensure quality and safety, which is paramount in structural steel construction.
Common Applications
Structural steel finds application in a broad range of construction projects. This includes commercial buildings, where structural steel supports not only the weight of the building but also enables the use of large open spaces without obstructive columns. It is also prevalent in the construction of industrial facilities, bridges, towers, and residential buildings. Beyond traditional uses, structural steel is increasingly employed in modern architectural designs, allowing for innovative shapes and designs that enhance visual appeal. Moreover, it’s commonly utilized in the form of beams, columns, and trusses, further demonstrating its adaptability and significance in diverse projects.
Advantages of Using Structural Steel
The benefits of using structural steel are manifold. One of the primary advantages is its strength; structural steel can carry weight that would be difficult for other materials like wood or concrete. This strength allows for longer spans and more open spaces within buildings. Additionally, structural steel is highly durable and resistant to many environmental factors, including moisture and pests, which often compromise wooden structures. The fabrication of steel components off-site can also speed up construction timelines, as well as improve safety and reduce waste at the construction site. Finally, structural steel is recyclable, providing a sustainable option that aligns with increasing environmental considerations in construction projects.
Planning and Designing for Structural Steel Construction
Initial Planning Phase Considerations
Before embarking on a structural steel construction project, thorough planning is crucial. Initial considerations involve site selection and understanding local zoning laws, which can impact the design and use of the structure. It is essential to evaluate the load requirements for the particular project, ensuring that the structural design can withstand both dead loads (the weight of the building itself) and live loads (temporary loads such as furniture and occupants). Collaborating with architects and engineers during this phase facilitates the integration of aesthetics and functionality, establishing a clear project direction. Another consideration is the budget, as costs will vary depending on materials, labor, and the complexity of the design.
Design Innovations in Structural Steel Construction
In recent years, design innovations have significantly influenced structural steel construction. Computer-aided design (CAD) software has allowed for greater accuracy and efficiency in drafting plans. Building Information Modeling (BIM) further enhances this process by creating comprehensive digital representations of physical and functional characteristics. These advancements allow for more complex geometries and the integration of other materials, leading to more sustainable and aesthetic designs. Also, adaptive reuse, where existing structures are repurposed for new uses, has gained popularity, demonstrating the versatility of structural steel when retrofitting older buildings.
Compliance and Regulations to Note
Structural steel construction must adhere to numerous codes and regulations that prioritize safety and performance. The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) provides guidelines that dictate the design, fabrication, and erection of steel structures. Additionally, local building codes may impose specific requirements based on geographical and environmental factors, necessitating a thorough understanding before commencing a project. Compliance not only ensures safety but also assists in preventing legal and financial liabilities during and after construction.
Key Techniques in Structural Steel Construction
Modern Fabrication Processes
The fabrication of structural steel has evolved significantly with advancements in technology. Today’s processes often harness CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinery, which allows for precise cutting, drilling, and shaping of steel components. This precision reduces waste and enhances the overall quality of the fabrication. Furthermore, the use of modular construction techniques—where large sections of structures are prefabricated off-site—improves efficiency and safety on construction sites. These processes also allow for thorough quality checks and control over the materials used, leading to a stronger final product.
Assembly Methods and Techniques
Assembling structural steel is a unique process that demands skilled labor and meticulous planning. Techniques such as bolting, welding, and riveting are commonly employed to secure steel structures together. Each method has its advantages: welding provides a strong, continuous bond, while bolted connections allow for quicker assembly and easier disassembly when necessary. Safety is critical during the assembly process; workers are trained in proper lifting techniques and use of safety gear to mitigate risks associated with working at heights or handling heavy materials. Innovations like the use of drone technology for surveys and inspections further enhance the efficiency and safety of assembly processes.
Use of Technology in Construction
Integrating technology into structural steel construction continues to redefine industry practices. From virtual reality (VR) for design visualization to augmented reality (AR) that assists workers on-site with assembly instructions, technology enhances accuracy and productivity. Project management software plays a crucial role in tracking timelines, budgets, and resource allocation, ensuring that projects remain on schedule and within scope. Furthermore, the use of sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices allows real-time monitoring of structural integrity and environmental conditions, helping prevent potential issues before they arise.
Challenges in Structural Steel Construction
Environmental and Safety Concerns
While structural steel construction boasts many advantages, it is not without challenges. Environmental impact concerns arise due to the energy-intensive processes of steel production and fabrication. However, the industry is increasingly adopting practices that prioritize sustainability, such as sourcing recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient techniques. Additionally, safety remains a top priority, as construction sites can present numerous hazards—working at heights, heavy material handling, and equipment operation. Continuous training and adherence to safety protocols are crucial in mitigating these risks.
Project Management Challenges
Managing a structural steel construction project involves coordinating multiple teams and stakeholders, which can be complex. Effective communication is necessary to ensure that all parties are aligned with project goals and timelines. Delays can arise from unforeseen circumstances, such as weather conditions or supply chain issues. Implementing robust project management practices, such as regular status meetings and employing agile methodologies, can help teams remain adaptable and responsive to challenges. Additionally, using advanced scheduling tools can enhance tracking and resource management.
Mitigating Risks during Construction
Risk management is an essential aspect of any construction project, especially in structural steel construction. Identifying potential risks early in the planning phase allows teams to develop mitigation strategies. Regular site inspections and audits can identify safety hazards, ensuring compliance with regulations and reducing the likelihood of accidents. Moreover, having contingency plans for potential delays or budget overruns is crucial for keeping projects on track. Engaging with a well-trained workforce and fostering a culture of safety further enhances risk management efforts.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Construction
Innovative Materials and Sustainability
The future of structural steel construction lies in continued innovation, particularly in sustainable practices. Emerging materials such as high-strength steel and composite materials promise to enhance performance while reducing the carbon footprint of construction projects. The trend toward green building practices emphasizes the importance of lifecycle assessments and sustainable material sourcing, including the use of recycled steel. Many industry leaders are investing in research to improve steel’s energy efficiency during production and exploring alternative fabrication methods to reduce waste.
Digital Transformation in the Industry
Digital transformation is rapidly shaping the landscape of structural steel construction. The adoption of cloud-based project management tools facilitates collaboration across diverse teams, enabling instantaneous updates and communication. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning can enhance predictive analytics, allowing teams to foresee project risks and make data-driven decisions. This shift toward a more data-centric approach can streamline operations and significantly boost overall efficiency, redefining traditional construction methodologies.
Global Trends Influencing Structural Steel Construction
Globalization is intensifying competition and collaboration in the structural steel construction industry. Markets worldwide are witnessing innovative techniques, materials, and building practices that can be adapted to local contexts. As countries worldwide strive to improve infrastructure and urban development, new opportunities arise in emerging markets for structural steel. Furthermore, international standards and regulations are evolving, necessitating a more global perspective for engineers and architects to ensure compliance and harness the best practices from around the globe.